What is Mindfulness?
Health is Wealth ( small changes, Big Impact )

Mindfulness is the state of being fully present in the present moment and aware of what is going on around you.
Mindfulness is the fundamental human ability to be fully present, aware of where we are and what we are doing and not become too reactive or overwhelmed by what is happening around us.
While mindfulness is something we all have, it becomes more accessible to us when we practice it on a daily basis.
It involves being fully engaged in whatever you’re doing, experiencing your thoughts, emotions and sensations as they arise without getting caught up in them or reacting impulsively.
Let us delve a little more into it. The human being is one of the best species ever created. The skill of living is not found on the outside but rather within the soul. I always says that excellent habits form great and amazing characters.
There’s an very famous that, you all have heard ‘ Yesterday is history, future is a mystery, but today is present, which is why it is called the present ‘. Living in the present moment brings you alive on the inside.
Mindfulness is a multidimensional notion with roots in different philosophical and spiritual traditions, most notably Buddhism.
Master the art of mindfulness.
Components:-
Deliberate awareness

At its heart, mindfulness is concerned with deliberate awareness. It is about concentrating your attention to the present moment and observing your sensations without becoming unduly attracted to or swept away by them. This deliberate awareness might include your thoughts, emotions, body sensations and even your surroundings.
Non-Attachment

Mindfulness promotes a non-attachment position in which you observe your thoughts and feelings without clinging to them or attempting to drive them away. This method cultivates a sense of detachment from the never-ending stream of mental chatter and emotional changes.
Moment-to-moment experience

Mindfulness emphasizes living life in the present moment. This is in contrast to our natural desire to concentrate on the past or project into the future. You can build a richer and more real life experience by completely interacting with the present.
Master the art of mindfulness.
Awareness Impermanance

Mindfulness frequently entails recognizing the impermanence of all sensations, both joyful and painful. This insight can assist in alleviating pain produced by an overabundance of attachment to joyful experiences or an aversion to discomfort.
Acceptance

Mindfulness promotes accepting things as they are, including your thoughts, feelings and circumstances. This does not imply resignation or inactivity, but rather accepting reality without adding extra resistance or judgment.
inter connected

Mindfulness can also promote a sense of connectivity or interdependence. You may begin to recognize the ways in which everything is connected and interrelated as you become more attuned to your experiences and the world around you.
Master the art of mindfulness.
Self-compassion

Mindfulness practise entails treating oneself with kindness and self-compassion. Instead of criticizing oneself for having specific ideas or feelings, you learn to approach yourself with the same understanding and compassion that you would offer to a friend.
evolving awareness

Mindfulness is a skill that develops with time and with practise. It may be difficult to maintain concentrated attention at first, but with constant effort, you can develop more mindfulness and present in various facets of your life.
mindful living

While mindfulness meditation is a structured practise, the ultimate goal is to integrate awareness into your daily life. This includes being conscious during normal activities, relationships and even problems, which allows you to behave intelligently rather than impulsively.
mindfulness as a way of being

Mindfulness can go beyond mere practise and become a way of being in the world. It entails establishing a profound feeling of awareness, knowledge and honesty in your ideas, actions and interactions.
Master the art of mindfulness.
Why should i bother paying attention on Mindfulness?

Being mindful appears to be generally useful. Mindfulness meditation has been shown in studies to reduce depression, distraction, anxiety, rumination, and emotional reactivity while improving information processing abilities, resilience, cognitive flexibility, immune function, intuition, emotion regulation, and relationship satisfaction.
Companies such as Google, LinkedIn, Monsanto, Aetna and many others provide mindfulness programmes to their staff for these and other reasons. Mindfulness is also essential for developing emotional intelligence, which has been found to be essential for being an exceptionally good leader or manager.
Mindfulness practise is a worthwhile investment in our general well-being. Mindfulness provides a shelter of calm and clarity in a fast-paced world riddled with distractions. We arm ourselves with strategies to manage stress, reduce anxiety and improve emotional regulation by adopting the practice of mindfulness.
Another NIH-funded study found that mindfulness practices can lower anxiety and aggression in urban kids, resulting in less stress, fewer disputes, and improved relationships. One significant advantage of mindfulness is that it helps you to pay attention to your thoughts, activities and body.
Not Paying Attention To Mindfulness Can lead To Various disadvantages:
increased stress

Ignoring mindfulness can lead to increased stress. You may become overwhelmed by daily pressures and obstacles if you lack the ability to manage stress and the awareness to identify its sources.
Master the art of mindfulness.
anxiety and depression

A lack of mindfulness might contribute to an increase of anxiety and depression symptoms. Negative thought patterns and emotional responses that are not addressed may lead to greater emotions of helplessness and despair.
Impaired emotional regulation

Emotional regulation might become challenging without attention. Unchecked emotional reactions can lead to rash behaviour, broken relationships and trouble dealing with disappointments.
Distracted and fragmented attention

When there is a lack of attention, the mind can become fragmented and distracted. You may find it difficult to concentrate on tasks, resulting in lower productivity and a diminished sense of accomplishment.
Master the art of mindfulness.
Missed self-discovery Opportunities

Being mindless can prohibit you from discovering your inner world. You may miss out on possibilities for personal growth, learning and good change if you are not self-aware.
strained relationships

Relationships can suffer when people are not fully present in interactions. Misunderstandings, disputes and a sense of alienation from loved ones can result from a lack of focused listening and true connection.
Unhealthy coping relationships
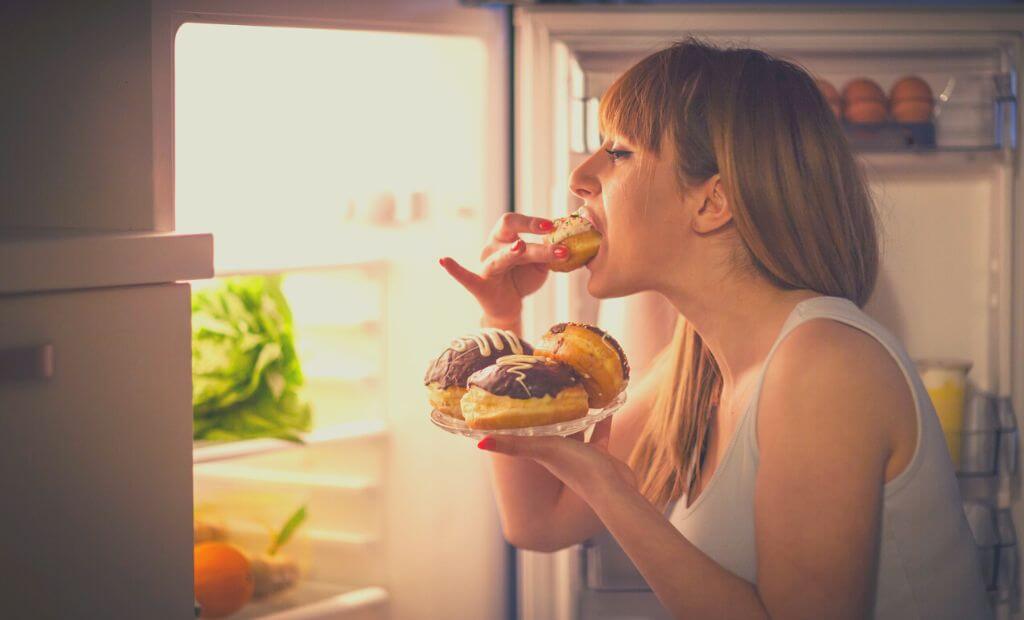

Mindlessness can lead to a reliance on unhealthy coping techniques, such as overeating, substance misuse or excessive screen time, as a way to escape from painful feelings or situations.
repetitive negative thoughts patterns
Negative thought patterns can persist if mindfulness is ignored. Rumination and self-criticism may become ingrained, resulting in a negative self-image and low self-esteem.
Mastery the art of mindfulness.
reduced self care

Mindlessness can lead to a lack of self-care habits. Ignoring your physical and mental well-being can lead to a loss in health and an overall sense of unfulfilment.
Missed current-moment appreciation

Living without awareness means missing out on the richness of the current moment. You may neglect to appreciate life’s simple joys and become consumed with regrets about the past or concerns about the future.
Lack of adaptability

Being unmindful can impair your ability to adapt to change. Without a thoughtful viewpoint, you may struggle to effectively negotiate transitions and unanticipated problems.
reduced resilience

A lack of mindfulness can lead to decreased resilience to setbacks. Due to a lack of inner resources, you may find it difficult to recover from problems and setbacks.
In summary, ignoring mindfulness might lead to a less meaningful and more difficult life experience. Mindfulness allows you to completely engage with life, negotiate problems with greater clarity and build a sense of well-being that pervades all aspects of your life.
Master the art of mindfulness.

Overcoming Harm OCD: Mindfulness and CBT Tools for Coping with Unwanted Violent Thoughts (16pt Large Print Edition)
People with harm OCD-a form of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)-suffer from violent, unwanted thoughts and a crippling fear of harming others. They may also resist seeking treatment for fear of being judged. In Overcoming Harm OCD, psychotherapist and OCD expert Jon Hershfield offers powerful cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness tools to help readers break the endless cycle of pain and self-doubt caused by their disorder, and overcome their most debilitating symptoms.
Are awareness and meditation synonymous?

Awareness and meditation are notions that are linked but not synonymous. They are frequently used in conjunction and can compliment one another, particularly in various meditation practises, yet they refer to slightly different aspects of mental and cognitive processes.
Awareness
Awareness is the state of being aware of something, whether it be your ideas, feelings, sensations or the outside environment. It entails being conscious of your internal and external experiences without passing judgement.
From being aware of your physical sensations (such as the sensation of your breath or the sense of your body) to being aware of your thoughts and emotions as they occur, awareness can span a wide range of experiences.
Meditation
Meditation is a collection of practises or procedures used to enhance mental traits such as awareness, focus and inner serenity. Meditation frequently entails focusing your attention on a single object, such as your breath, a mantra or a specific sensation.
Meditation’s goal can differ according on the tradition or practice, but it generally attempts to promote mental clarity, reduce stress, increase self-awareness and foster a sense of well-being.
Meditation can benefit from increased awareness. Many meditation practices, particularly mindfulness meditation, entail growing awareness of one’s thoughts, feelings and body sensations without becoming involved in them.
Meditation can help you acquire a greater degree of awareness in this situation by teaching your mind to observe these experiences without judgement or attachment.
To summarize, mindfulness and meditation are two distinct notions. Meditation frequently includes the practice of growing awareness, although awareness can be applied to various elements of life outside of the setting of meditation.
Relationship Between Awareness And Meditation?

Meditation and awareness have a tight and symbiotic relationship, particularly in mindfulness-based meditation practices.
Master the art of mindfulness.
Awareness as a Meditation Component
A essential component of many meditation practises is awareness. Meditation frequently entails conditioning your mind to be totally present and aware of your experiences, whether they are your breath, physiological sensations, thoughts or emotions.
You can obtain a better grasp of your mind and gain insights into the nature of your ideas and emotions by fostering this heightened awareness.
Mindfulness meditation
A noteworthy example of the relationship between awareness and meditation is mindfulness meditation. It focuses on developing nonjudgmental awareness of the present moment.
Practitioners direct their attention on their breath, physiological sensations or other anchor points and when their thoughts wander, they gently return their attention to the chosen place of focus.
This practise teaches you to become more aware of your thinking processes, increasing self-awareness and decreasing the inclination to react automatically.
Increasing concentration and clarity
Concentration-based meditation practises, such as focused-attention meditation, can improve awareness.
When you focus on a single point of emphasis, such as your breath, you become more sensitive to the nuances of that experience. This increased concentration causes a better awareness of subtleties that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Regular meditation
Regular meditation might help you have a broader perspective on life and events. You begin to examine your thoughts and emotions without reacting to them as you meditate and gain awareness.
Instead of being driven by spontaneous responses, this shift in perspective allows you to respond to events more wisely.
Integration into daily life
The awareness developed during meditation can be carried forward into your daily life. Consistent practise makes you more aware of your thoughts, feelings and behaviours in diverse situations.
This awareness can result in greater self-regulation, decision-making and emotional well-being.
Mutual Reinforcement
In a positive feedback loop, awareness and meditation reinforce each other. Meditation improves your ability to be mindful of your experiences.
As your awareness grows, your meditation practise becomes more successful because you can better watch and understand your mind’s oscillations.
Meditation, in essence, provides a systematic platform for deliberately cultivating consciousness.
This increased awareness evolves into a more thoughtful way of being over time, improving your general well-being and your ability to engage with the environment in a more intentional and balanced manner.
Master the art of mindfulness.
Why is mindfulness important?

Mindfulness is crucial for a variety of reasons, since it provides numerous benefits that assist both mental and physical well-being.
Mindfulness is extremely important because of its transformational effect on mental and emotional well-being. Mindfulness allows people to face life’s obstacles with better resilience and clarity by cultivating a nonjudgmental awareness of the present moment.
This practice relieves stress by removing people from their ruminations and worries, resulting in a sensation of serenity. Enhanced emotional regulation results from the ability to perceive emotions without reacting immediately, resulting in enhanced mental health and fewer anxiety and depression symptoms.
Furthermore, mindfulness increases self-awareness by assisting individuals in understanding their thoughts, emotions and behavioural patterns, resulting in personal progress. Mindfulness promotes cognitive functioning by sharpening focus, concentration and decision-making.
Physically, it is associated with reduced blood pressure, better sleep and a stronger immune system. Finally, mindfulness promotes a holistic approach to life by cultivating stronger relationships, improving general well-being and fostering a genuine appreciation for the beauty of the present moment.
What are the Physical and mental health benefits of meditation and Mindfulness?
Physically
Stress reduction
Meditation and mindfulness techniques are well-known for their ability to relieve stress by triggering the relaxation response and decreasing stress hormone production such as cortisol.
Master the art of mindfulness.
Blood pressure regulation
Regular practice can help lower high blood pressure and promote cardiovascular health, lowering the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Pain management
Mindfulness-based therapies have been shown to be useful in managing chronic pain disorders by altering people’s perceptions of pain and improving pain-coping techniques.
Immune system support
Meditation and mindfulness practises have been related to increased immune system functioning, perhaps leading to better resistance to infections and diseases.
Better sleep
Mindfulness meditation can help improve sleep quality and reduce insomnia by calming the mind and promoting relaxation.
Enhanced body awareness
Mindfulness practices encourage a heightened awareness of bodily sensations, which can lead to better self-care and early detection of physical discomfort or issues.
Mentally
Anxiety and depression reduction
Mindfulness-based therapies have been demonstrated to significantly reduce anxiety and depression symptoms. These practises assist people acquire perspective on their ideas and feelings allowing them to be less intense.
Emotional regulation
Regular meditation and mindfulness practise can improve emotional regulation, allowing people to respond to emotions in a more balanced and adaptive way.
Enhanced self-awareness
Mindfulness practises improve self-awareness by encouraging people to notice their thoughts, feelings and behaviours without judgement. This realisation can lead to personal development and self-awareness.
Reduced rumination
Mindfulness assists in breaking the loop of rumination (repetitive negative thinking) by refocusing attention to the present moment, hence reducing depressed symptoms.
Strengthened resilience
Meditation promotes mental resilience by teaching people to be present with issues rather than ignoring or reacting impulsively to them.
Master the art of mindfulness.
Improved focus and concentration
Regular meditation enhances attention span, focus, and cognitive flexibility, which can boost productivity and mental clarity.
Mind-body connection
Mindfulness practises promote awareness of the mind-body connection, which promotes overall health and balance.
Decreased psychological Distress
Mindfulness reduces symptoms of psychological discomfort while also promoting a sense of well-being and satisfaction.
Meditation and mindfulness practises provide a comprehensive approach to wellness that benefits both the mind and the body.
Medical and psychological communities are increasingly recognising the potential of these practises to supplement conventional therapy and improve general quality of life.
12 ways to Practice of Mindfulness?

1. Spend time out in nature
2. Practice breathing techniques
3. Check in with your emotions
4. Practice mindfulness ‘5,4,3,2,1’ with your senses
5. Take a mindful walk
6. Say positive affirmations
7. Spend time writing in a journal
8. Mindfully listen to music
9. Practice yoga and stretch
10. Draw colour or doodle
11. Take photos
12. Garden or do yard work
neurontin delivery overnight to US buying neurontin without a script neurontin to buy purchase cytotec in US no prescription neurontin prescriptian buy cheap neurontin generic pillpack by amazon pharmacy buy neurontin online US walmart home delivery pharmacy Recommended Pharmacies To purchase neurontin online without script needed buying generic neurontin Overnight cheap neurontin order pain meds online
Полностью свежие новости моды.
Актуальные эвенты известнейших подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, высокая мода.
Приятное место для модных хайпбистов.
https://malemoda.ru/
Несомненно актуальные новинки модного мира.
Все события мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, гедонизм.
Интересное место для модных хайпбистов.
https://fashionvipclub.ru/
Несомненно трендовые новости индустрии.
Актуальные события мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, haute couture.
Новое место для трендовых людей.
https://sneakero.ru/
Несомненно трендовые новости моды.
Важные события известнейших подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, гедонизм.
Интересное место для модных хайпбистов.
https://sneakerside.ru/
Точно трендовые новинки подиума.
Актуальные события мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, бренды, высокая мода.
Лучшее место для стильныех хайпбистов.
https://sneakersgo.ru/
Fresh watch news and events. Actual collections, models. All information about legendary watch companies.
https://chrono.luxepodium.com/
Стильные советы по подбору превосходных видов на любой день.
Статьи экспертов, новости, все новые коллекции и шоу.
https://rftimes.ru/news/2024-08-14-7-samyh-kultovyh-veshchey-ot-balenciaga
На нашем сайте доступны брендовые сумки Bottega Veneta. Здесь можно приобрести эксклюзивные модели, которые станут изюминкой вашего гардероба. Вся продукция отличается высочайшим качеством, что присуще бренду Боттега Венета
https://socialmediainuk.com/story19312417/bottega-veneta
Премиальный интернет-магазин Боттега Венета предлагает широкий ассортимент оригинальной продукции от итальянского бренда. Здесь вы сможете подобрать и заказать продукцию из новых коллекций с удобной доставкой по всей стране.
https://bottega-official.ru