How and why does malnutrition occur?
Health is Wealth ( Small Changes Big Impact )

Malnutrition is a major issue on a global scale. If we look closely, we can see that it is a global issue right now. But how and why is this happening? Well, there are numerous factors.
Malnutrition occurs when the body receives insufficient nutrition, either in quantity or quality, to sustain optimal health and function.
While the UNICEF-WHO-World Bank Group Joint Malnutrition Estimates 2023 show that stunting prevalence has been declining since 2000, more than one in five (148.1 million children under the age of five) were stunted in 2022, and at least 45.0 million were wasting at any given point in the year.
It can be caused by a variety of circumstances and underlying causes, resulting in both over nutrition (excessive intake of particular nutrients, frequently leading to obesity) and under nutrition (insufficient intake of critical nutrients, often leading to stunting, wasting or deficiencies).
Enumerate ways to prevent malnutrition?
Inadequate nutrient intake

This is a prevalent cause of malnutrition, especially in impoverished places or when food is scarce. Individuals may lack the resources needed for appropriate growth, development and maintenance if they do not have access to a balanced diet comprising vital nutrients such as proteins, carbs, fats, vitamins and minerals.
Poor dietary habits

A diet high in empty calories, sweets and processed foods and low in nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins can contribute to malnutrition. Even if caloric intake is adequate, a shortage of key nutrients might result in deficits and health problems.
digestive disorders

Malnutrition can be caused by medical problems that impact digestion, absorption or metabolism. Even if the diet is well-balanced, conditions such as celiac disease, Crohn’s disease and chronic diarrhoea can limit the body’s ability to absorb nutrients from meals.
Economic factors

Poverty and a lack of finances might make it difficult for people to eat a variety and nutritious diet. Inadequate income frequently leads to a reliance on cheaper, calorie-dense but nutrient-deficient foods, which contributes to malnutrition.
Enumerate ways to prevent malnutrition?
Lack of education

A lack of knowledge about healthy nutrition and dietary practises might result in bad food choices. This is especially true in communities with little nutrition education.
Infections and diseases
Certain infections and diseases can raise the body’s nutritional needs or interfere with vitamin absorption. Chronic infections, HIV/AIDS and various parasite diseases for example can all lead to malnutrition.
Environmental factors

Natural disasters, conflict and displacement can interrupt food supply networks and access to food, resulting in malnutrition among impacted communities.
diet disorders

Diet disorders, such as anorexia nervosa and bulimia, can cause severe malnutrition as a result of restrictive diet, excessive activity or purging behaviours.
Enumerate ways to prevent malnutrition?
aging

Malnutrition can occur in the elderly due to decreased appetite, impaired digestion and diminished nutritional absorption.
Lifestyle choices
Excessive alcohol intake, smoking and drug abuse can all impair nutritional absorption and utilisation, contributing to malnutrition.
Malnutrition can have serious health repercussions, including weaker immune systems, stunted growth, cognitive deficits, increased susceptibility to infections and even death.
Malnutrition must be addressed through a multifaceted approach that involves increasing access to nutritious foods, encouraging balanced diet education, addressing underlying health issues and raising awareness about the need of good nutrition for individual and community well-being.
Major globally problems related to malnutrition?

Malnutrition causes a number of serious global issues that affect people’s health, well-being, and development. On a worldwide basis, some of the major concerns associated to malnutrition include:-
Child stunting and wasting

Childhood malnutrition can result in stunting (impaired growth and development) and wasting (extreme weight loss). Stunted children are more likely to experience delays in cognitive and physical development, limiting their future potential and production.
Enumerate ways to prevent malnutrition?
Maternal and infant health

Pregnancy malnutrition can lead to low birth weight kids and maternal problems. Undernourished newborns are more susceptible to illness and developmental delays, perpetuating a cycle of poor health.
Micro-nutrient deficiencies

A deficiency in key vitamins and minerals (micronutrients) such as vitamin A, iron, iodine, and zinc can cause a variety of health problems such as decreased immune function, anaemia, and developmental difficulties.
Obesity and non-communicable diseases
Malnutrition is more than just undernutrition; overnutrition and obesity are rising global issues. Obesity is exacerbated by diets heavy in processed foods, sweets and unhealthy fats, as well as an increased risk of noncommunicable diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease and certain malignancies.
Economic impact

Malnutrition can have a huge economic impact on countries. Lost productivity as a result of ill health, increased healthcare expenditures and lower educational attainment as a result of hunger can all stymie a country’s growth and development.
Enumerate ways to prevent malnutrition?
Global hunger

Despite progress, millions of people continue to suffer from hunger owing to a lack of adequate and nutritious food. Poverty, warfare and natural catastrophes frequently worsen food insecurity.
child mortality

Malnutrition is a major cause of child mortality, particularly in underdeveloped nations. Children that are malnourished are more susceptible to infections and illnesses, resulting in a greater mortality rate.
educational impairment

Malnourished children frequently suffer from cognitive deficits, shorter attention spans and poor learning ability. This can jeopardise their academic success and limit their future chances.
Interplay and climate change

Climate change can have an impact on food production and availability, potentially leading to food shortages and increasing hunger, especially among vulnerable groups.
Enumerate ways to prevent malnutrition?
Healthcare system strain
Malnutrition creates a strain on healthcare systems since treating and managing malnutrition-related illnesses necessitates significant resources and infrastructure.
Inequity and vulnerable people

Malnutrition affects marginalised people disproportionately, including women, children, rural communities and those living in poverty. Malnutrition must be addressed with an emphasis on equity and reaching the most vulnerable people.
Long term development implications

Countries with high rates of malnutrition confront difficulties in meeting sustainable development goals. Malnutrition can stifle economic growth, limit educational attainment and perpetuate poverty cycles.
Addressing global malnutrition issues necessitates a multifaceted approach that includes increasing access to nutritious foods, promoting healthy diet education, strengthening healthcare systems, addressing poverty, ensuring clean water and sanitation and fostering international cooperation to address the underlying factors that contribute to malnutrition in its various forms.
Is malnutrition chronic?

Malnutrition can be acute or chronic, depending on the origin and duration of the disease.
Enumerate ways to prevent malnutrition?
Acute malnutrition is defined as a severe and unexpected lack of appropriate nutrition over a brief period of time. It frequently results in fast weight loss, muscle atrophy and obvious indications of nutritional inadequacy.
Acute malnutrition is especially harmful for children and can evolve to potentially fatal illnesses such as severe acute malnutrition (SAM).
SAM is distinguished by extreme weight loss, muscle wasting and edoema (swelling caused by fluid retention). To treat acute malnutrition, prompt intervention with therapeutic diets and medical care is crucial.
Chronic malnutrition often known as under nutrition or stunting, is a long-term disorder caused by a constant lack of necessary nutrients over an extended period of time. It can impede children’s growth and development, resulting in stunted physical and cognitive development.
Chronic malnutrition is defined by a failure to attain the predicted height and weight for a child’s age, and its consequences can be permanent, affecting an individual’s total potential and well-being throughout their life.
Obesity and Over nutrition: On the other end of the spectrum, over nutrition is a chronic condition characterised by excessive calorie consumption, which frequently leads to obesity and other health concerns.
Over nutrition is a type of malnutrition because of an imbalance in nutrient intake. Obesity raises the risk of a number of noncommunicable diseases, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease and some malignancies.
It is crucial to remember that malnutrition is not limited to any particular region or demography; it happens worldwide and can affect people of all ages.
Malnutrition’s causes and consequences are diverse and multifaceted, involving topics such as food access, diet quality, healthcare, education and socioeconomic variables.
To combat malnutrition, comprehensive efforts must be made to improve nutrition education, promote access to diverse and nutritious meals, ensure clean water and sanitation and address broader social and economic health determinants.
Causes of malnutrition?
Depending on the type of malnutrition, the related causes are as follows:
Poor dietary intake
Mental health problems such as depression or schizophrenia alter your mood and the desire to eat, leading to a poor appetite.
Alcoholism
Alcohol contains calories which in turn can reduce the patient’s desire to eat enough to supply the body with essential nutrients. Also, alcohol leads to damage to liver which is the storehouse of proteins and vitamins
Eating disorders like anorexia and bulimia.
Enumerate ways to prevent malnutrition?
Protein energy malnutrition or PEM
The two types of PEM are described as –
Kwashiorkor: which occurs when there is not enough protein in the diet
Marasmus: which occurs when the diet is inadequate in both calories and protein
Digestive disorders
Conditions that disturb your ability to digest food such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
Dementia
A brain disease that leads to a gradual decrease in the ability to think and remember and this affects a person’s daily functioning. Patients often forget to eat meals for hours together.
Lack of breastfeeding
Leads to malnutrition in infants and children.
Economic status
Those who are poor are at risk of under-nutrition; on the other hand, those who have high socio-economic status are more likely to be over-nourished
What Are the Malnutrition Symptoms and Signs?

Unintentional weight loss is seen as the first indicator of malnutrition. The signs and symptoms differ depending on the reason.
Enumerate ways to prevent malnutrition?
The signs and symptoms of malnutrition are as follows:-
- Without activity, you can lose 5-10% of your overall body weight.
- Tiredness and dizziness
- Slim or bloated?
- Nails that are brittle or spooned
- Wound healing takes time.
- Skin may be pale, thick, dry and prone to bruising.
- Bones that are soft and sensitive
- Joint pain
- Disturbances in vision
- Anaemia
- Goitre (enlargement of the thyroid gland)
- Twitches in the muscles
- Loss of reflexes and lack of muscular coordination
- Scaling and cracking of the lips and mouth
- Malnourished children will be short and thin for their age and will have a weak immune system
malnutrition can be prevented or controlled by many ways:-

Consider our experts recommendations to prevent malnutrition :-
Encourage nutrition education

- Raise public awareness about the need of a well-balanced diet and appropriate nutrition through public health campaigns, school programmes and community workshops.
- Provide information on the nutritional worth of various foods as well as the benefits of eating a range of nutrient-rich foods.
Increase food accessibility and Availability

- To ensure a consistent supply of fresh and diversified foods, support local agriculture and food production.
- Create techniques for making nutritious foods more inexpensive and accessible, especially for vulnerable groups.
- Implement food distribution programmes in places where there is a high level of food insecurity.
Enumerate ways to prevent malnutrition?
Nutritional assistance for vulnerable populations

- To ensure optimal growth and development, provide tailored nutrition treatments for pregnant and breastfeeding mothers, babies and young children.
- Implement school feeding programmes to guarantee that students are well fed while at school.
Breast feeding education

- Breast milk gives critical nutrients to infants, thus encourage and support exclusive breastfeeding throughout the first six months of life.
- To ensure successful breastfeeding, moms should be given lactation assistance and information.
Supplementation of micro-nutrients

- To address micronutrient deficiencies, provide vitamin and mineral supplements to persons at risk of specific deficiencies, such as pregnant women and children.
Sanitation and clean water
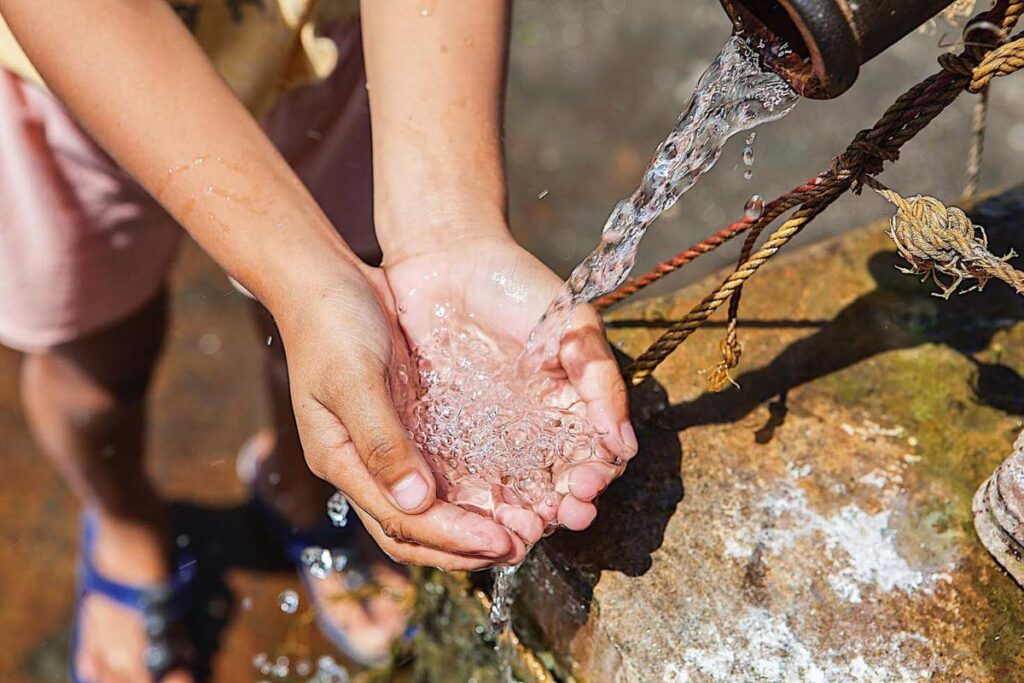

- Improve access to safe drinking water and sanitation facilities in order to reduce waterborne diseases and infections that lead to malnutrition.
Enumerate ways to prevent malnutrition?
Medical services
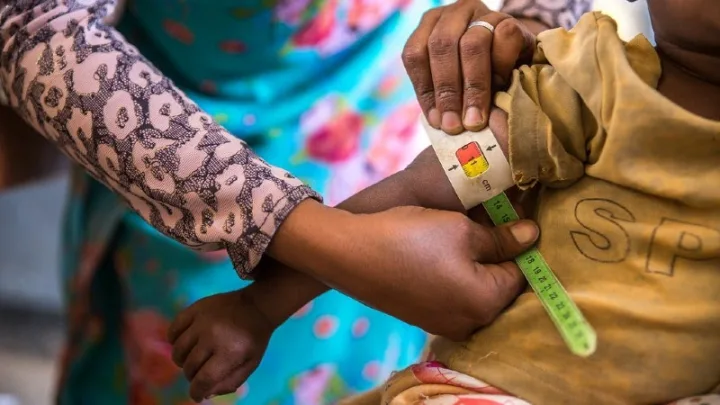
- Improve healthcare systems so that children and pregnant women may receive frequent check-ups, growth tracking and dietary counselling.
- Treat and manage medical issues such as gastrointestinal disorders and infections that can lead to malnutrition.
encourage hygiene and sanitation

- Educate communities on basic hygiene practises to help reduce the spread of illnesses that can lead to malnutrition.
Support for agricultural development

- To increase the availability of nutritious foods, invest in agricultural practises that promote diversified and nutrient-rich crop cultivation.
Women must be empowered

- Empower women by providing them with educational and economic possibilities, as educated and empowered women are more likely to make healthy choices for themselves and their families.
Enumerate ways to prevent malnutrition?
Safety nets for the poor
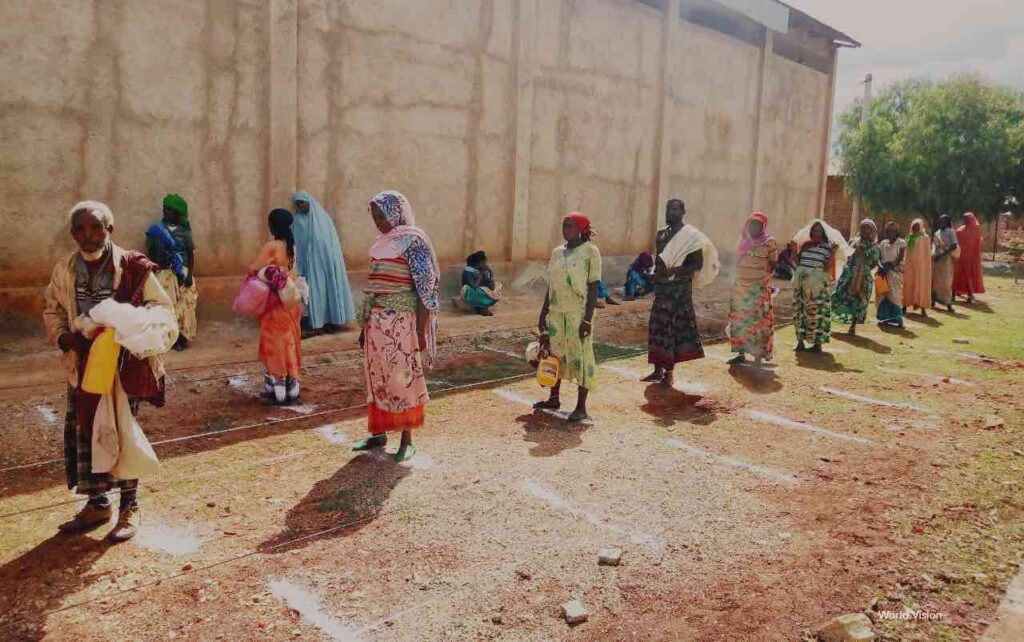

- Implement social welfare programmes that provide financial assistance to needy groups, allowing them to access nutritional foods and healthcare.
Combat poverty and inequality

- Address broader socioeconomic problems that contribute to malnutrition, such as poverty, illiteracy and a lack of access to healthcare and nutritional foods.
regulate unhealthy food marketing

- Implement regulations to limit the marketing of unhealthy and processed foods to youngsters in particular.
Encourage healthy lifestyles

- To avoid obesity and other health problems, promote physical activity and discourage sedentary behaviour.
Advocacy and collaboration

- Encourage governments, non-governmental organisations, international organisations and the corporate sector to work together to prevent and reduce malnutrition.
Preventing and treating malnutrition necessitates a comprehensive and integrated approach that considers the various factors influencing dietary choices, food access, healthcare and socioeconomic conditions.
To have a long-term positive impact, effective tactics should be customised to the individual circumstances and needs of distinct groups.
Модные заметки по созданию модных луков на любой день.
Заметки профессионалов, события, все дропы и шоу.
https://heyjinni.com/read-blog/134739
На данной платформе вы можете купить изделия бренда знаменитого бренда Loro Piana. Каталог товаров включает эксклюзивные изделия, изготовленные с учётом высококачественных материалов и передовых технологий. Погрузитесь в атмосферу стиля и комфорта, который предлагает итальянский дом Loro Piana.
https://loropiana.whitezorro.ru